FAQ
FAQ
Frequency Asked Question
Media routinely used in ocular microbiology media are routinely used in ocular microbiology are:- Blood agar (BA), Chocolate agar (CA), Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA), Nutrient agar (NA), Non-nutrient agar (NNA) with E. coli overlay, and Thioglycollate broth.
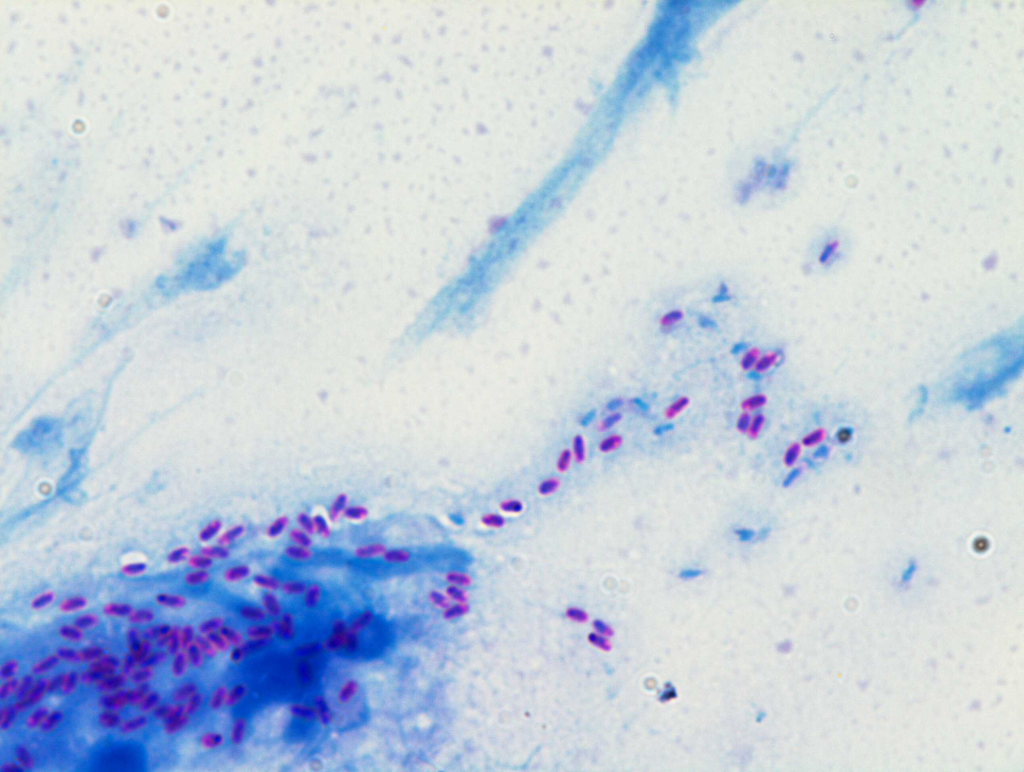
Blood Agar is preferred in ocular samples because it supports a wide range of bacteria, including Gram-positive cocci, and helps detect hemolysis, which is useful for differentiation
the purpose of Chocolate Agar in eye infections is to supports growth of fastidious organisms such as Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae,important ocular pathogens
Enrichment media enhance the growth of pathogens when present in small numbers. Example: Brain Heart Infusion Broth or Thioglycollate broth for intraocular fluids.
Solid media help isolate colonies and observe morphology, while liquid media enhance growth from low inoculum or sterile-site samples.
Generally, Pythium insidiosum is resistant to conventional antifungals (azoles, amphotericin B, natamycin) because it lacks ergosterol in its cell membrane. This is the key reason why patients often worsen under standard fungal keratitis therapy.
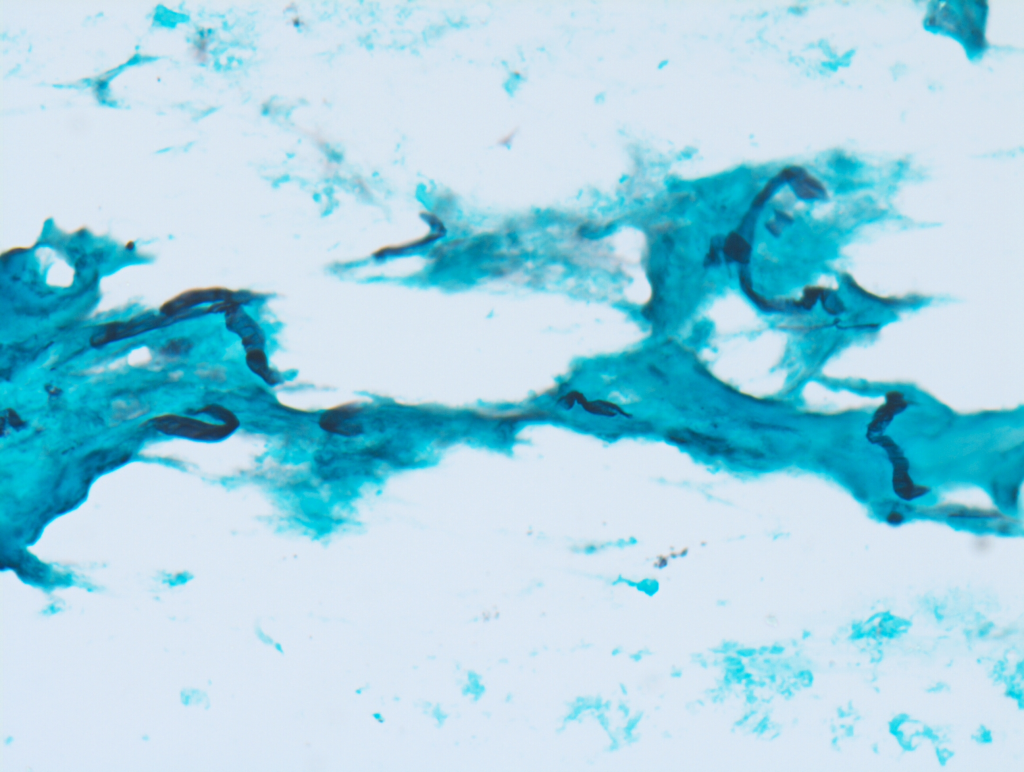
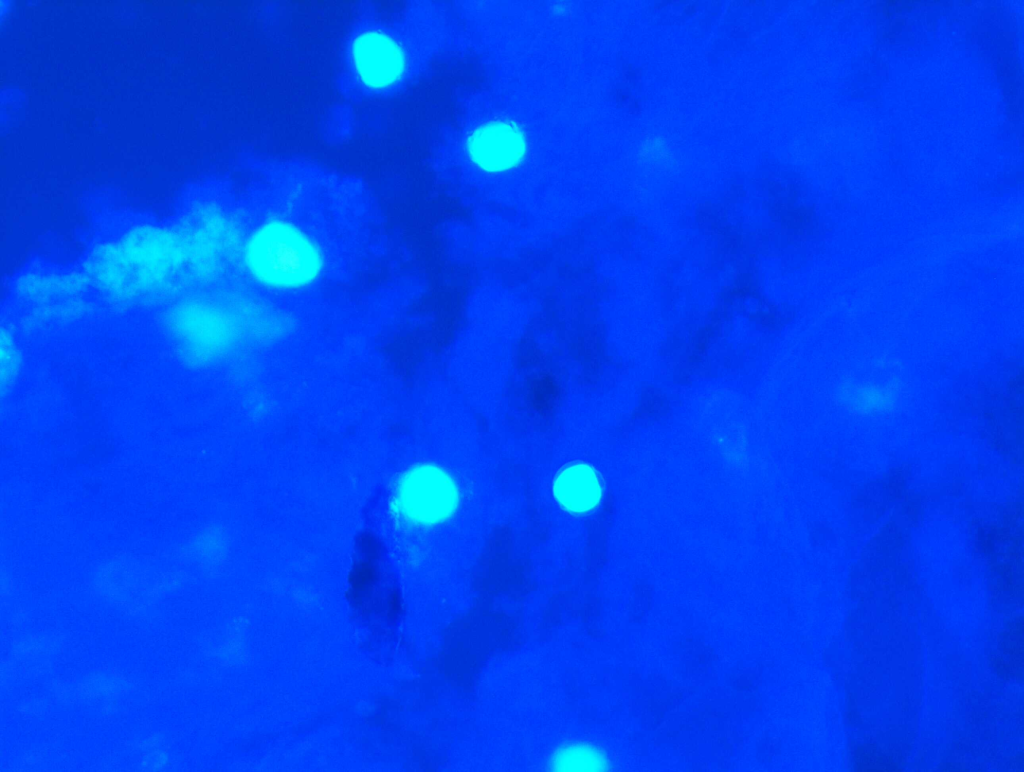
It is used to detect Acanthamoeba, a protozoan causing severe keratitis, especially in contact lens users.
Different microorganisms have varied nutritional needs. Using selective, differential, enriched, and specialized media allows accurate isolation, identification, and study of diverse bacteria, fungi.
Selective media inhibit unwanted microbes and allow target organisms (e.g., MacConkey agar for Gram-negative bacilli). Differential media distinguish between organisms based on biochemical reactions
(e.g., lactose fermentation on MacConkey shows pink colonies)
PHMB (Polyhexamethylene Biguanide) is a polymeric biguanide antiseptic commonly used as a disinfectant in swimming pools and contact lens solutions. In ophthalmology, it is widely used as a topical 0.02% eye drop for treating Acanthamoeba keratitis.
PHMB disrupts microbial cell membranes by binding to phospholipids, leading to leakage of cytoplasmic contents and cell death. It is particularly effective against Acanthamoeba cysts and trophozoites, bacteria, and some fungi.
Chlorhexidine is a bisbiguanide antiseptic, used at 0.02% concentration as topical eye drops for Acanthamoeba keratitis and as an alternative to PHMB. It has broad-spectrum activity against Gram-positive, Gram-negative bacteria, and protozoa.
Zoospores are motile, flagellated spores produced by Pythium insidiosum. They are the infective stage responsible for corneal infection, especially in patients exposed to contaminated water or soil. Zoospores encyst, adhere to the corneal surface, and germinate, causing tissue invasion.